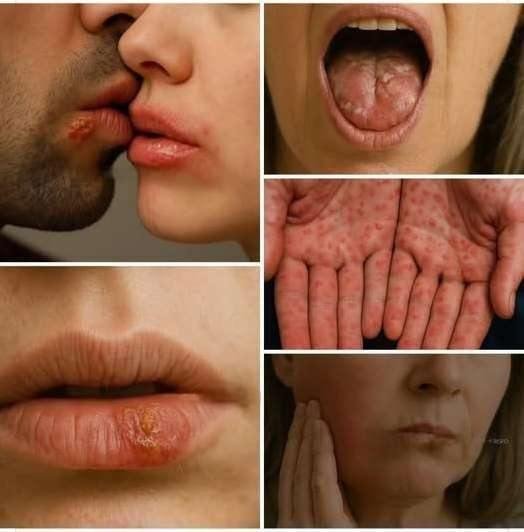
Understanding Herpes Labialis (Cold Sores)
Herpes labialis, commonly known as cold sores or fever blisters, is a widespread viral infection caused primarily by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). These small, fluid-filled blisters typically appear on or around the lips, and are often recurrent.
Causes and Transmission
Herpes labialis is highly contagious and is most often spread through direct contact with infected saliva or skin. The virus enters the body through small breaks in the skin or mucous membranes and can remain dormant in nerve cells for years.
Common triggers for reactivation include:
-
Fever or illness
-
Sun exposure
-
Stress or fatigue
-
Hormonal changes (e.g., menstruation)
-
Immunosuppression
Symptoms
The initial outbreak of herpes labialis may be more severe, especially in children. Symptoms include:
-
Tingling or burning sensation before the sore appears
-
Painful blisters that burst and crust over
-
Swelling and redness around the affected area
-
Occasional fever, swollen lymph nodes, or sore throat
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on the appearance of the sores. In uncertain cases, a doctor may perform:
-
A viral culture
-
PCR testing
-
Blood tests for HSV antibodies
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for herpes simplex virus, outbreaks can be managed with antiviral medications such as:
-
Acyclovir
-
Valacyclovir
-
Famciclovir
These can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, especially if taken early. Over-the-counter creams and pain relievers may also provide relief.
Prevention Tips
To minimize the risk of spreading or triggering outbreaks:
-
Avoid kissing or sharing items during an active outbreak
-
Use sunscreen on the lips to prevent sun-induced flare-ups
-
Practice good hygiene
-
Consider antiviral prophylaxis for frequent outbreaks
Conclusion
Herpes labialis is a common condition that, while not life-threatening, can be painful and socially distressing. Understanding its triggers, transmission, and treatment options can help individuals manage the condition effectively and reduce recurrence.